关键词:激光等离子体、laser-produced plasmas、放电等离子体、discharge-produced plasmas、
辐射加热等离子体、radiatively-heated plasmas、激波传播、shock propagation、Z-pinches
一 软件介绍
HELIOS是一款一维辐射-流体力学模块,用于研究辐射等离子体流体力学演化,也可以用来研究激光束或外部辐射源加热的平面、圆柱或球形等离子体演化。软件易用是设计HELIOS时重点,以用户友好图形界面创建问题、监控模拟过程、以及查看模拟结果。
HELIOS可以和棱镜公司的其他实验室等离子体分析模块配合使用,包括:
![]() HydroPLOT是一款绘图工具,用于显示来自于HELIOS的大量模拟结果;
HydroPLOT是一款绘图工具,用于显示来自于HELIOS的大量模拟结果;
![]() VISRAD是一款三维view factor软件,用于OMEGA和NIF激光装置、以及Z pulsed-power和Z-Pinch装置上设计实验。VISRAD包括用于创建靶和定向激光CAD功能,以及计算贯穿整个三维靶系统辐射环境。对于网格中任意给定的表面元,HELIOS可以用VISRAD提供的随时间和频率变化的入射通量数据来模拟外部辐射源的影响。
VISRAD是一款三维view factor软件,用于OMEGA和NIF激光装置、以及Z pulsed-power和Z-Pinch装置上设计实验。VISRAD包括用于创建靶和定向激光CAD功能,以及计算贯穿整个三维靶系统辐射环境。对于网格中任意给定的表面元,HELIOS可以用VISRAD提供的随时间和频率变化的入射通量数据来模拟外部辐射源的影响。
![]() SPECT3D是一款碰撞-辐射光谱分析和成像软件包,通过HELIOS预测的时间相关等离子体结果,用SPECT3D进行后处理,产生可以和试验测量相比的图像和光谱。
SPECT3D是一款碰撞-辐射光谱分析和成像软件包,通过HELIOS预测的时间相关等离子体结果,用SPECT3D进行后处理,产生可以和试验测量相比的图像和光谱。
二、HELIOS主要特点
HELIOS是一款易用的一维辐射-流体力学程序代码,可以模拟如下领域流体力学:
![]() 激光等离子体
激光等离子体
![]() 放电等离子体(Z-pinches)
放电等离子体(Z-pinches)
![]() 辐射加热等离子体
辐射加热等离子体
![]() 激波在材料中传输
激波在材料中传输
HELIOS-CR是HELIOS的增强版本,包括采用一个内联碰撞-辐射(inline collisional-radiative)(C-R)模型模拟非局部热力学平衡(non-LTE*)等离子体力学。
三、HELIOS和HELIOS-CR主要特点
进行平面、圆柱和球形等离子体1-D模拟仿真
拉格朗日坐标系中能量和质量守恒方程(例如网格随流体移动)
包括易用的图形用户界面(GUI)用于创建问题和监控模拟过程。
包括图形应用软件HydroPLOT,用于模拟结果可视化。
![]() 以线图、2-D彩色等高线图和3D表面图等方式查看结果
以线图、2-D彩色等高线图和3D表面图等方式查看结果
![]() 编辑和保存制图设置
编辑和保存制图设置
![]() 复制和粘贴图表到MS Office应用程序中
复制和粘贴图表到MS Office应用程序中
用于一种温度(T
电子传导限流时,采用如下方法执行等离子体热传导:
![]() Spitzer传导率
Spitzer传导率
![]() 表格的SESAME格式传导率(tabular conductivity)
表格的SESAME格式传导率(tabular conductivity)
![]() 用户指定(常数)传导率
用户指定(常数)传导率
![]() Spitzer 和常数混合型传导率
Spitzer 和常数混合型传导率
包括能量沉积模型用于:
![]() 激光沉积
激光沉积
![]() 磁流体动力学(MHD)效应(仅限于圆柱形几何体)
磁流体动力学(MHD)效应(仅限于圆柱形几何体)
![]() 离子束
离子束
![]() 外部辐射源
外部辐射源
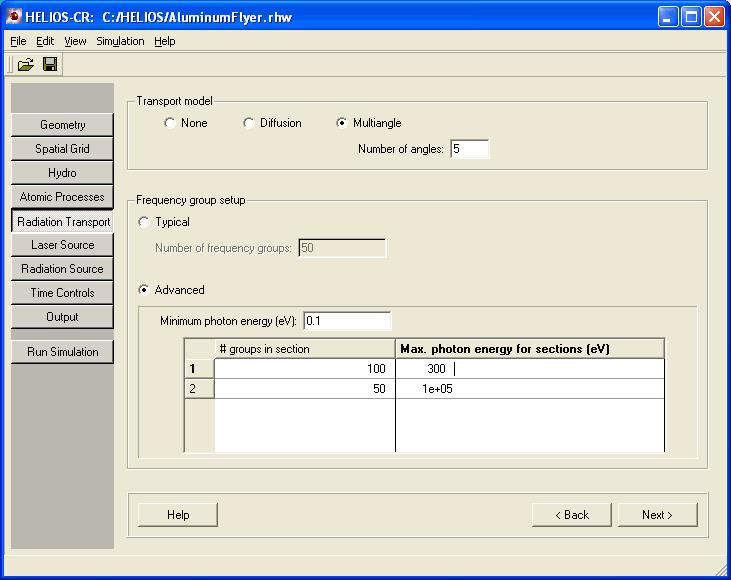
采用下列任意一个模型进行多光子能量组辐射传输计算:
![]() 限流辐射扩散
限流辐射扩散
![]() Multi-angle short characteristics (仅限于平面几何形状)
Multi-angle short characteristics (仅限于平面几何形状)
支持使用SESAME状态方程、热传导和电阻率数据库
支持使用Prism不透明度和状态方程(PROPACEOS)数据库
包括计算聚变产物产额和速率选项
在碰撞-辐射模拟**中,包括下列原子过程
![]() 碰撞电离、复合、激发和退激
碰撞电离、复合、激发和退激
![]() 光致电离和受激复合
光致电离和受激复合
![]() 光致激发和受激发射
光致激发和受激发射
![]() 自发衰减
自发衰减
![]() 辐射复合
辐射复合
![]() 双电子复合、自动电离和电子俘获
双电子复合、自动电离和电子俘获
利用ATBASE原子数据库支持:
![]() 光电离截面
光电离截面
![]() 振子强度
振子强度
![]() 碰撞电离截面
碰撞电离截面
![]() 碰撞激发截面
碰撞激发截面
![]() 原子能级能量和跃迁能量
原子能级能量和跃迁能量
![]() 双电子复合、自电离和电子俘获率
双电子复合、自电离和电子俘获率
与Prism的其他应用程序接口:
![]() SPECT3D基于辐射-流体力学模拟结果产生光谱和图像,并与实验光谱和成像数据对比。
SPECT3D基于辐射-流体力学模拟结果产生光谱和图像,并与实验光谱和成像数据对比。
![]() HydroPOLT是一款绘图工具用于查看计算结果
HydroPOLT是一款绘图工具用于查看计算结果
![]() VISRAD用于产生时间和频率相关的外部辐射源的输入文件
VISRAD用于产生时间和频率相关的外部辐射源的输入文件
*LTE = local thermodynamic equilibrium
**HELIOS-CR application only.
四、HELIOS用户界面
Prism软件容易使用,图形用户界面方便设置,交互式图形容易显示大量结果。不需要专门学习程序语言、编写代码,用户只需要通过键盘和鼠标既可以完成挑战性项目模拟仿真。使用HELIOS有多方便?部分用户评语可以告诉您:
Dr. Leslie Welser, Scientist at Los Alamos National Laboratory
“…, 我想告诉你们我对HELIOS印象有多么深刻:这是一款不可思议的软件,我上午安装软件,下午就进行了实际模拟;而采用另一款软件我需要花数周的时间才能学会如何正确使用…“
Prof. David Cohen, Dept. of Physics and Astronomy, Swarthmore College.
“我和我的学生一直使用PRISM系列软件从事项目研究,我的学生成功地使用HELIOS, SPECT3D, PrismSPECT, VISRAD来模拟大量实验室试验及天体物理等离子体。我的学生能够在一天内掌握该软件,这主要得益于软件的直观、清晰、简单易用的图形化界面及内含的渲染工具….我现在已经在用部分模块进行教学。”
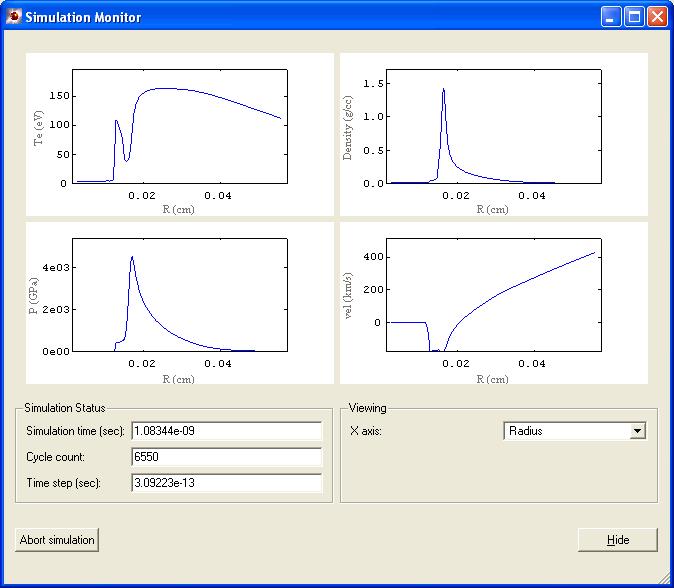
Helios自动设置网格 Helios进程监控
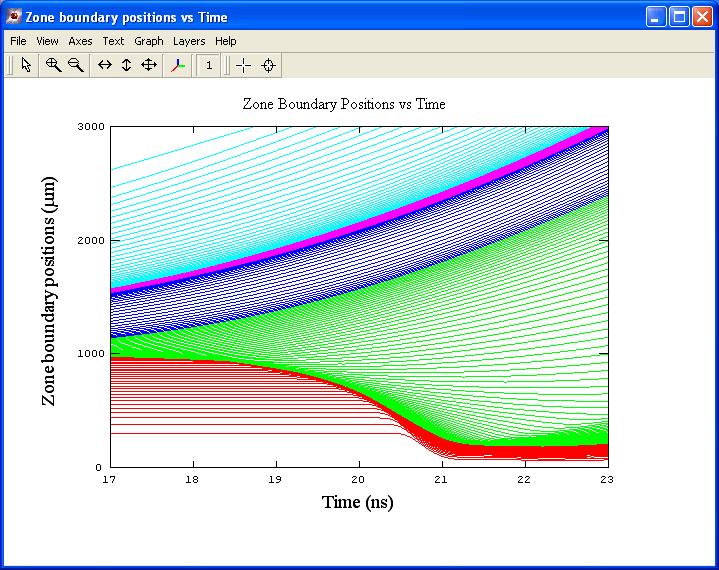
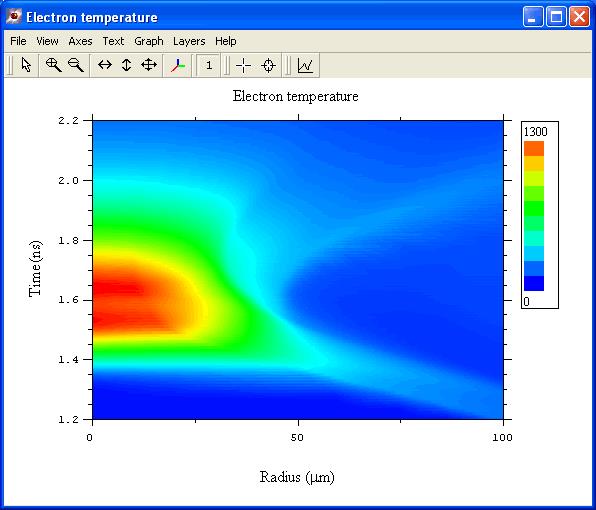
质量运动 温度等值线图
五、安装平台要求
HELIOS和HydroPLOT采用交叉平台C++用户界面开发的,HELIOS和HydroPLOT也采用OpenGL图形应用框架。使用交叉平台UI软件和OpenGL允许HELIOS和HydroPLOT支持MS Windows, Unix, and Mac 平台。HELIOS和HydroPLOT当前支持:
- MS Windows (7, XP, NT, 98/2000)
- Linux(Redhat, Suse, Knoppix, and Mandrake)
- Mac OSX. (10.7 and above)
六、HydroPLOT
HydroPLOT是一款图形工具,用于显示HELIOS和HELIOS-CR的各种计算结果。HydroPLOT利用PrismPLOT图表库来显示:线图表、2-D彩色等高线图、3-D曲面图。采用HydroPLOT,用户可以显示:
![]() Quantity values vs. position at selected simulation times
Quantity values vs. position at selected simulation times
![]() Quantity values vs. time for selected spatial zones
Quantity values vs. time for selected spatial zones
![]() Quantity values vs. frequency for selected times and zone boundaries
Quantity values vs. frequency for selected times and zone boundaries
![]() 2-D color contour plots and 3-D surface plots of:
2-D color contour plots and 3-D surface plots of:
-
Quantity values vs. position and time
-
Quantity values vs. frequency and time
-
Quantity values vs. frequency and position
七、全球参考用户
国家实验室和研究所
大学用户:

企业用户:
八、参考文献、说明手册
HELIOS自带在线文件和可以快速运行的案例,绝大部分窗口界面有帮助按钮,可直接跳到相关帮助页面。
HELIOS Reports and Whitepapers
![]() HELIOS-CR -- A 1-D Radiation-Magnetohydrodynamics Code with Inline Atomic Kinetics Modeling
HELIOS-CR -- A 1-D Radiation-Magnetohydrodynamics Code with Inline Atomic Kinetics Modeling
Research Papers
![]() Emission properties of ns and ps laser-induced soft x-ray sources using pulsed gas jets
Emission properties of ns and ps laser-induced soft x-ray sources using pulsed gas jets
![]() Characteristics of Argon Plasma Waveguide Produced by Alumina Capillary Discharge for Short- Wavelength Laser Application
Characteristics of Argon Plasma Waveguide Produced by Alumina Capillary Discharge for Short- Wavelength Laser Application
![]() XUV Spectroscopic Characterization of Warm Dense Aluminum Plasmas Generated by the Free-Electron-Laser FLASH
XUV Spectroscopic Characterization of Warm Dense Aluminum Plasmas Generated by the Free-Electron-Laser FLASH
![]() Generation of Scaled Protogalactic Seed Magnetic Fields in Laser-Produced Shock Waves
Generation of Scaled Protogalactic Seed Magnetic Fields in Laser-Produced Shock Waves
![]() Tendency of Spherically Imploding Plasma Liners Formed by Merging Plasma Jets to Evolve Toward Spherical Symmetry
Tendency of Spherically Imploding Plasma Liners Formed by Merging Plasma Jets to Evolve Toward Spherical Symmetry
![]() Hot Electron Temperature and Coupling Efficiency Scaling with Prepulse for Cone-Guided Fast Ignition
Hot Electron Temperature and Coupling Efficiency Scaling with Prepulse for Cone-Guided Fast Ignition
![]() Measurement of the Adiabatic Index in Be Compressed by Counterpropagating Shocks
Measurement of the Adiabatic Index in Be Compressed by Counterpropagating Shocks
![]() Radiation Hydrodynamic Simulation of a Photoionised Plasma Experiment at the Z Facility
Radiation Hydrodynamic Simulation of a Photoionised Plasma Experiment at the Z Facility
![]() High-Resolution Radial Ka Spectra Obtained from a Multi-keV Electron Distribution in Solid-Density Titanium Foils Generated by Relativistic Laserematter Interaction
High-Resolution Radial Ka Spectra Obtained from a Multi-keV Electron Distribution in Solid-Density Titanium Foils Generated by Relativistic Laserematter Interaction
Two-color Thomson Scattering at FLASH
![]() Development of X-ray Thomson Scattering for Implosion Target Characterization
Development of X-ray Thomson Scattering for Implosion Target Characterization
![]() Two-Fluid Electromagnetic Simulations of Plasma-Jet Acceleration with Detailed Equation-of-State
Two-Fluid Electromagnetic Simulations of Plasma-Jet Acceleration with Detailed Equation-of-State
![]() In-Flight Measurements of Capsule Shell Adiabats in Laser-Driven Implosions
In-Flight Measurements of Capsule Shell Adiabats in Laser-Driven Implosions
Soft X-ray sScattering Using FEL Radiation for Probing Near-Solid Density Plasmas at Few Electron Volt Temperatures
![]() Ion Velocity Distribution Measurements in a Magnetized Laser Plasma Expansion
Ion Velocity Distribution Measurements in a Magnetized Laser Plasma Expansion
![]() Anti-diffusive Radiation Flow in the Cooling Layer of a Radiating Shock
Anti-diffusive Radiation Flow in the Cooling Layer of a Radiating Shock
![]() X-ray Radiography and Scattering Diagnosis of Dense Shock-Compressed Matter
X-ray Radiography and Scattering Diagnosis of Dense Shock-Compressed Matter
![]() Thomson Scattering on Inhomogeneous Targets
Thomson Scattering on Inhomogeneous Targets
![]() Plasmons in Strongly Coupled Shock-Compressed Matter
Plasmons in Strongly Coupled Shock-Compressed Matter
![]() Interactive Tools Designed to Study Mix in Inertial Confinement Fusion Implosions
Interactive Tools Designed to Study Mix in Inertial Confinement Fusion Implosions
![]() Temperature Measurement Through Detailed Balance in X-ray Thomson Scattering
Temperature Measurement Through Detailed Balance in X-ray Thomson Scattering
![]() Thomson Scattering in Dense Plasmas with Density and Temperature Gradients
Thomson Scattering in Dense Plasmas with Density and Temperature Gradients
![]() Radiation and Hot Electron Temperature Measurements of Short-Pulse Laser Driven Hohlraums
Radiation and Hot Electron Temperature Measurements of Short-Pulse Laser Driven Hohlraums
![]() Inference of ICF Implosion Core Mix Using Experimental Data and Theoretical Mix Modeling
Inference of ICF Implosion Core Mix Using Experimental Data and Theoretical Mix Modeling
![]() Ultrafast Kα X-ray Thomson Scattering From Shock Compressed Lithium Hydride
Ultrafast Kα X-ray Thomson Scattering From Shock Compressed Lithium Hydride
![]() Evolution of Elastic X-ray Scattering in Laser-Shocked Warm Dense Lithium
Evolution of Elastic X-ray Scattering in Laser-Shocked Warm Dense Lithium
![]() Measurements of Ionic Structure in Shock Compressed Lithium Hydride from Ultrafast X-Ray Thomson Scattering
Measurements of Ionic Structure in Shock Compressed Lithium Hydride from Ultrafast X-Ray Thomson Scattering
![]() X-ray Thomson Scattering in High Energy Density Plasmas
X-ray Thomson Scattering in High Energy Density Plasmas
![]() Probing Warm Dense Lithium by Inelastic X-ray Scattering
Probing Warm Dense Lithium by Inelastic X-ray Scattering
![]() Application of Fall-Line Mix Models to Understand Degraded Yield
Application of Fall-Line Mix Models to Understand Degraded Yield
![]() Laser Assisted Heating of Extreme Ultraviolet-Emitting Z-Pinch Plasmas
Laser Assisted Heating of Extreme Ultraviolet-Emitting Z-Pinch Plasmas
![]() Experimental Characterization of Picosecond Laser Interaction with Solid Targets
Experimental Characterization of Picosecond Laser Interaction with Solid Targets
![]() Bremsstrahlung and Line Spectroscopy of Warm Dense Aluminum Plasma Heated by XUV Free-Electron-Laser Radiation
Bremsstrahlung and Line Spectroscopy of Warm Dense Aluminum Plasma Heated by XUV Free-Electron-Laser Radiation
![]() Studies of Plastic-Ablator Compressibility for Direct-Drive Inertial Confinement Fusion on OMEGA
Studies of Plastic-Ablator Compressibility for Direct-Drive Inertial Confinement Fusion on OMEGA
![]() Ultrafast X-ray Thomson Scattering of Shock-Compressed Matter
Ultrafast X-ray Thomson Scattering of Shock-Compressed Matter
![]() Development of Two Mix Model Postprocessors for the Investigation of Shell Mix in Indirect Drive Implosion Cores
Development of Two Mix Model Postprocessors for the Investigation of Shell Mix in Indirect Drive Implosion Cores
![]() Spectroscopic Determination of Temperature and Density Spatial Profiles and Mix in Indirect-Drive Implosion Cores
Spectroscopic Determination of Temperature and Density Spatial Profiles and Mix in Indirect-Drive Implosion Cores
![]() Measurement and Modeling of the Implosion of Wire Arrays with Seeded Instabilities
Measurement and Modeling of the Implosion of Wire Arrays with Seeded Instabilities
![]() Application of Fall-Line Mix Models to Understand Degraded Yield
Application of Fall-Line Mix Models to Understand Degraded Yield
![]() Spectroscopic Analysis and NLTE Radiative Cooling Effects in ICF Capsule Implosions with Mid-Z Dopants
Spectroscopic Analysis and NLTE Radiative Cooling Effects in ICF Capsule Implosions with Mid-Z Dopants
![]() Dopant Radiative Cooling Effects in Indirect-Drive Ar-Doped Capsule Implosion Experiments
Dopant Radiative Cooling Effects in Indirect-Drive Ar-Doped Capsule Implosion Experiments
![]() Radiation-Hydrodynamics, Spectral, and Atomic Physics Modeling of Laser-Produced Plasma EUV Lithography Light Sources
Radiation-Hydrodynamics, Spectral, and Atomic Physics Modeling of Laser-Produced Plasma EUV Lithography Light Sources
![]() Modeling of Indirect-Drive ICF Implosions Using a 1-D Hydrodynamics Code with Inline Collisional-Radiative Atomic Kinetics
Modeling of Indirect-Drive ICF Implosions Using a 1-D Hydrodynamics Code with Inline Collisional-Radiative Atomic Kinetics
Memos
![]() Radiation-Driven Shock in Aluminum
Radiation-Driven Shock in Aluminum
![]() Radiation-Driven Capsule Implosions in Z-Pinch Dynamic Hohlraums
Radiation-Driven Capsule Implosions in Z-Pinch Dynamic Hohlraums
![]() Diffusion and Multi-Angle Radiation Transport Model Benchmarks
Diffusion and Multi-Angle Radiation Transport Model Benchmarks
九、应用实例
Laser-heated foil, Radiation-heated foil, Radiation-driven shock, Radiation-driven capsule implosion, Laser-driven capsule implosion, Radiation Burnthrough.
模拟实例一:Laser-heated foil
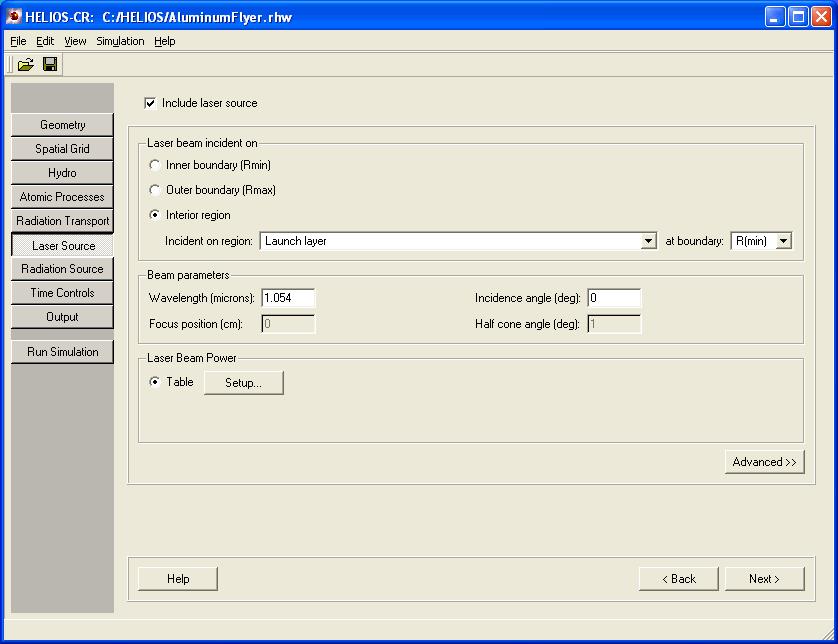
In this calculation, an 80 ns long laser beam (fluence: 50 J/cm2, wavelength: 1.054 mm) is used to accelerate an Al flyer.
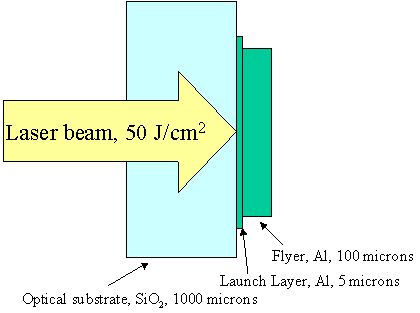
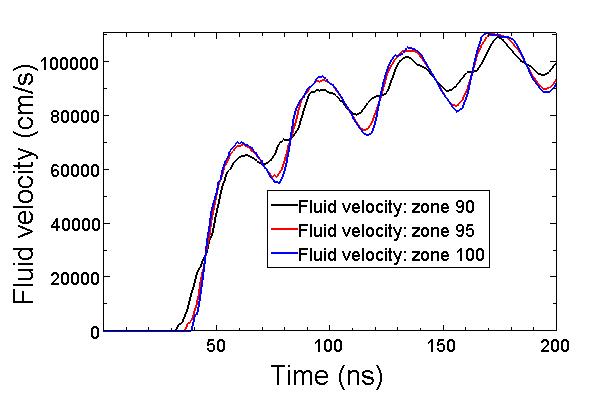
模拟实例二:Radiation-Heated Al Foil
In this calculation, radiation heats a plastic-tamped Al foil.
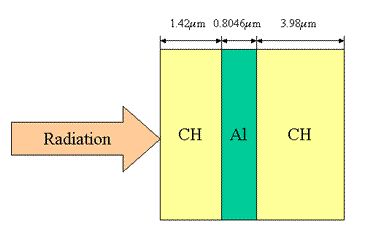
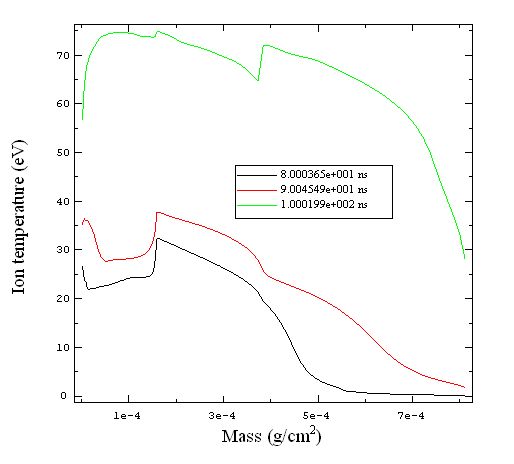
模拟条件 模拟结果
模拟实例三:Radiation-Driven Shock in Al Plate
In this calculation, an external radiation source drives a strong shock through an Al plate.
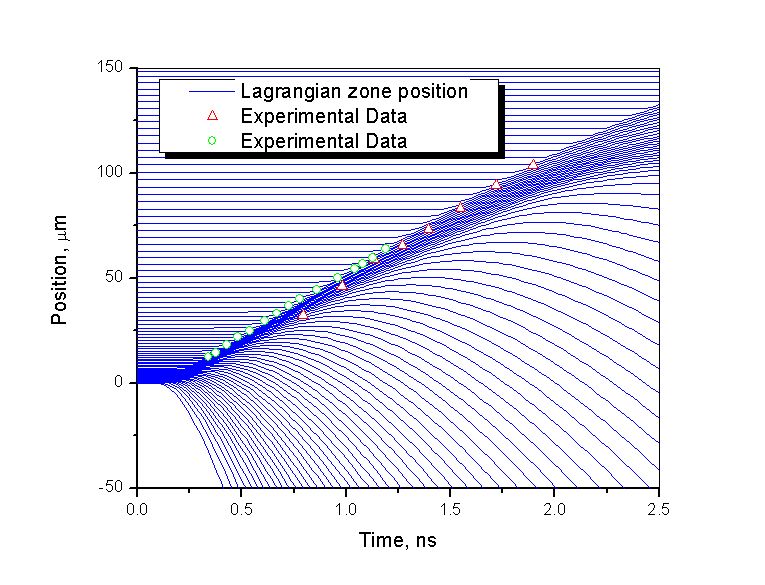
模拟实例四:Radiation-Driven Capsule Implosion
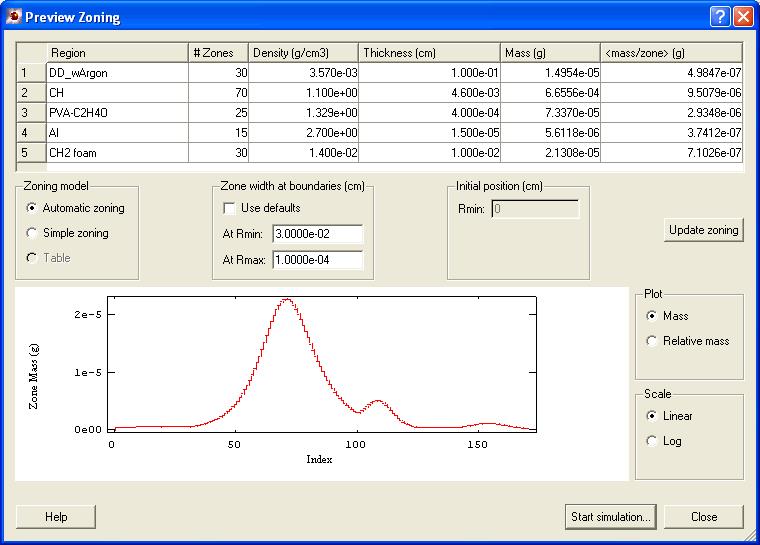
In this calculation, a plastic micro balloon (wall thickness - 35 micron, internal diameter - 220 micron) is filled with 50 atm DD. The capsule is driven by 200 eV radiation for 1 nanosecond. This system is representative of indirectly drive n capsule implosion experiments at OMEGA.
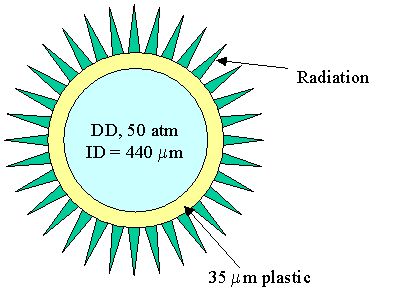
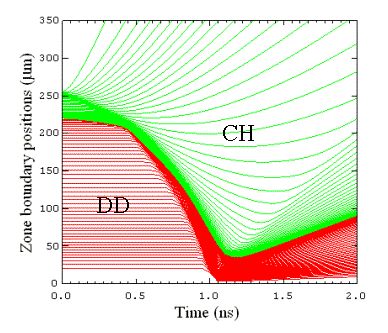
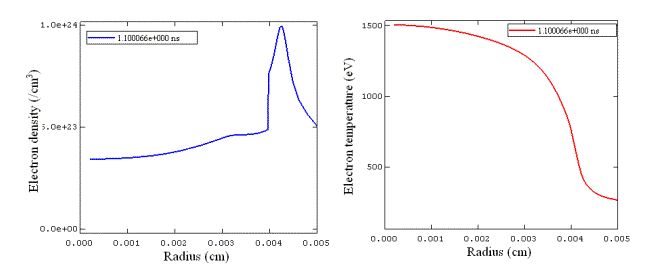
模拟实例五:Laser-Driven Capsule Implosion :In this calculation, a plastic micro balloon (wall thickness – 22.6 micron CH, outer diameter – 939.2 micron) is filled with 10 atm DD and 0.059 atm of Ar. The capsule is driven by a 1 nanosecond square pulse with a 0.15 ns rise. Total power delivered to the target is 23 kJ. The laser is assumed to have 4 degree half cone angle, and focused 0.5 cm (~ 5 diameers) behind the target. This system is representative of directly driven capsule implosion experiments at OMEGA.
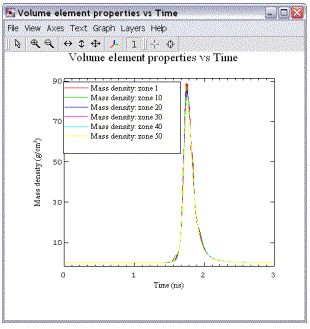
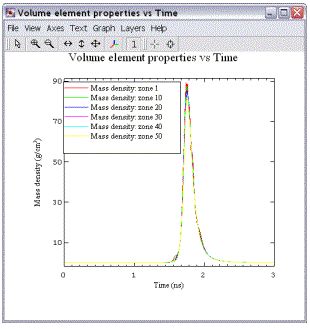
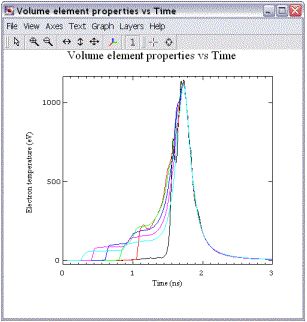
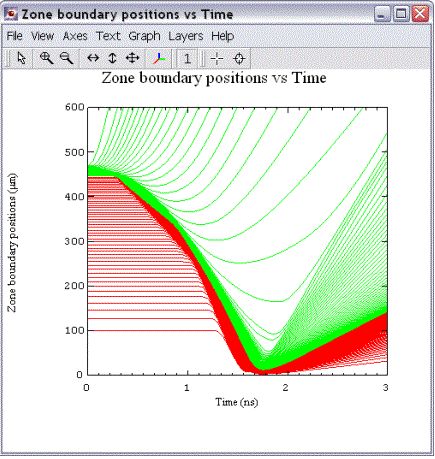
模拟实例六:Radiation Burn Through SiO2 Foam:In this calculation, an external radiation source burns through a SiO2 foam
上海续波光电技术有限公司
网站:www.cwopto.com 邮箱:info@cwopto.com
电话:86 021 60342238 移动:86 155 02170017